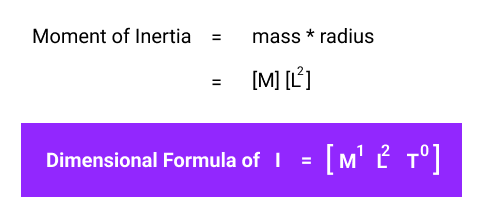
The dimensional formula of Moment of Inertia is
[ M1 L2 T0 ]
where [M], [L], and [T] are the fundamental quantities: Mass, Length, and Time.
From the above formula, we can derive the dimensions of the moment of inertia as (1, 2, 0).
How to calculate the dimensional formula of the moment of inertia?
We can derive this formula using the definition of the moment of inertia.
In physics, we can define the moment of inertia as the force required to stop a rotating body. Suppose a body is rotating along an axis; mathematically, the moment of inertia is the sum of the product of masses and squared radius of different particles of the body.
Moment of Inertia (I) = m1r12 + m2r22 + m3r32 + …
This is equivalent to,
I = mass * radius2Dimensionally, we use
- [M] for mass
- [L] for radius
Now the formula becomes
Moment of Inertia (I) = [M1] * [L2]
Since the formula doesn’t include the fundamental quantity Time, we can use [T0], which is equal to 1.
Moment of Inertia (I) = [M1] * [L2] * [T0]
Hence, the dimensional equation of moment of inertia is I = [ M1 L2 T0 ].
Related Articles