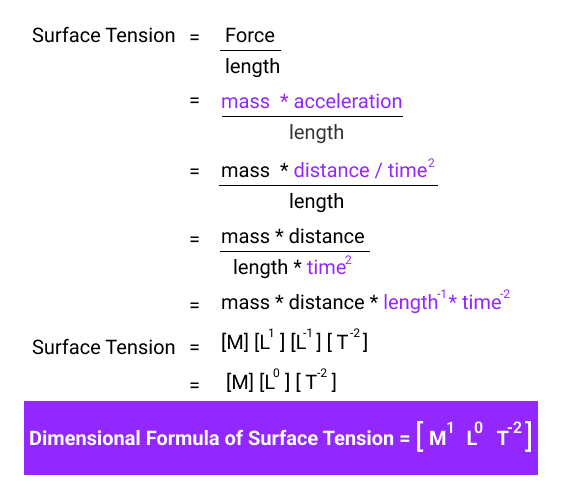
The dimensional formula of Surface Tension is
[ M1 L0 T-2 ]
where [M], [L], and [T] are the fundamental quantities: Mass, Length, and Time.
From the above formula, we can derive the dimensions of work as (1, 0, -2).
How to calculate the dimensional formula of surface tension?
We can derive this formula using the definition of surface tension.
In physics, we can define surface tension as the total energy needed to increase the unit surface area of a liquid. Suppose a force acts on a particular length, then mathematically,
Surface Tension (T) = Force / length
We know that Force = mass * acceleration. Substituting the value of Force in the above equation, we get
T = (mass * acceleration ) / length
We know
- acceleration = speed / time
- speed = distance / time
- acceleration = distance / time2
Therefore,
Surface Tension (T) = mass * (distance / time2 ) / length
T = (mass * distance) / (time2 * length)
T = mass1 * distance1 * time-2 * length-1Dimensionally, we use
- [M] for mass
- [L] for distance and length
- [T] for time
Now the formula becomes
Surface Tension (T) = [M1] * [L1] * [T-2] * [L-1]
T = [M1] * [T-2]
Since the formula doesn’t include the fundamental quantity Length, we can use [L0], which is equal to 1.
Surface Tension (T) = [M1] * [L0] * [T-2]
Surface Tension (T) = [M1] * [L0] * [T-2]
Hence, the dimensional equation of surface tension is T = [ M1 L0 T-2 ].
Related Articles