Air pollutants are unwanted substances that enter the atmosphere from various natural and anthropogenic sources. They can be in solid, liquid, or gaseous form.
The pollutants substances are harmful to our health and surroundings. It can be divided into:
1. Primary Pollutants
Pollutants that are emitted into the atmosphere directly are known as primary pollutants.
For example, carbon monoxide emitted from vehicle exhaust and sulfur dioxide from industries are primary pollutants.

2. Secondary Pollutants
Secondary pollutants do not enter the air directly but are rather formed in the atmosphere after the reactions between primary pollutants.
For example, harmful ozone is a secondary pollutant that is formed by the reaction between nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds.
To learn more about types of air pollution, visit Types of Air Pollution.
6 Harzadous Air Pollutants
The more widely found air pollutants have been classified as criteria pollutants worldwide. There are six common hazardous air pollutants that have been placed in this classification. They are as follows
1. Carbon monoxide(CO)
Carbon monoxide gas is tasteless and has no smell so it is hard to detect. If we inhale enough concentration of the gas, it becomes very harmful to us.
What are the sources of CO?
CO is emitted into the atmosphere from
- Vehicle exhaust
- Manufacturing processes in industries
- Tobacco smoke
- Volcanoes
- Forest Fires
What are the effects of CO?
- When a high amount of CO enters our body, it reduces oxygen in our red blood cells which hamper the functions of organs.
- It causes clumsiness and increased fatigue.
- It also increases the risks of a heart attack in people with a history of heart problems.
- Infants and children are more affected.

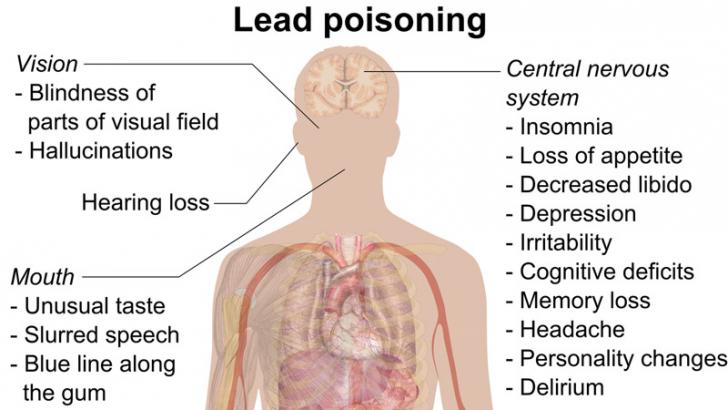
2. Lead
Lead is a heavy metal that occurs naturally on the earth’s surface. It is found in the air in a concentration not more than 0.1 microgram/m3.
What are the sources of Lead?
There are many anthropogenic sources of lead such as
- Mining and manufacturing of metal and concrete
- Leaded Petrol, coal, ceramic products, car batteries, and paints
What are the effects of Lead?
- Lead is stored in our teeth and bones.
- It can impart damage to our vital organs like brain, liver and kidneys.
- Exposure to varying level of lead can cause acutte or chronic leald poisoning.
- It can have adverse effects in our immune system, cardiovascular system and reproductive system.
3. Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide reacts with other substances easily and forms harmful compounds like sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid. It has a pungent smell and almost 99% of the gas is emitted into the air by human activities.
What are the sources of Sulfur dioxide?
- The main sources are industrial activities such as production of electricity from fuels containing sulfur.
- Fuel combustion in power plants.
- Extraction of metals.
- Emissions from automobiles
What are the effects of Sulfur dioxide?
- It irritates the airways and causes wheezing, coughing and difficulty in breathing.
- Worsen asthama.
- Forms small particles after reaction with compunds and these particles can enter our airways causing adverse effects.
- It can aggravate respiratory diseases like emphysema and worsen heart diseases.
4. Harmful ozone
It is the ozone found near ground level that is harmful to us. It is formed by the reaction between nitrogen oxides and various volatile organic compounds when sunlight is present.
What are the sources of harmful ozone?
Major sources are:
- Emission from Industries
- Exhaust from Automobiles
- Chemical Solvents
- Oil Refining
- Petrochemicals
- Bush Fires
What are the effects of harmful ozone?
- Exposure to enough levels causes irritation and pain in eyes, throat and nose.
- It reduces lung function.
- Causes respiratory ailments like difficulty in breathing and coughing.
- It can also aggravate existing problems of asthama.

5. Particulate matter
Particulate matter (PM) is a mix of extremely small fine or coarse particles. It is the main component of particle pollution which is one of the major types of air pollution.
What are the sources of particulate matter?
Particulate matter can enter the atmosphere from several sources such as:
- Automobile exhaust
- Industrial Emissions
- Burning of Fossil Fuels
- Tobacco smoke
- Forest Fire
- Farming
- Road Construction
What are the effects of particulate matter?
- Particles of small size can be inhaled into our lungs and can even enter the bloodstream.
- Particle pollution can aggravate diseases of lung, heart and respiratory ailments.
- It causes difficulty in breathing and irritation of respiratory tract.
6. Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
NO2 is a highly reactive gas and is used as an indicator of nitrogen oxides. It is one of the major air pollutants that caused photochemical smog that we see in most of our cities.
What are the sources of Nitrogen dioxide?
Common sources are:
- Buring of Fossil Fuels
- Automobile Exhaust
- Metal Refining
- Food Processing
- Gas Heaters
Some of these gas is also formed by the action of lightening and chemical processes in plants and soil.
What are the effects of Nitrogen dioxide?
Exposure of different levels causes:
- Airway Inflammation
- Worsen Asthama
- Bronchitis and Emphysema
- Aggravate diseases of the heart
Related Articles